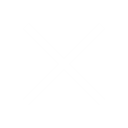
X-Ray vs CT vs MRI
Need for X-Ray Scan
X rays are used for several diverse purposes:
Patient preparation before an X ray is very basic and minimal. You may be asked to wear a gown during the exam, depending on which area is being X-rayed. You may also be asked to remove jewelry, eyeglasses and any metal objects because they can show up on an X-ray.
Benefits of X-Ray Scan
X rays are a non-invasive and painless way to diagnose and monitor health problems.
They can effectively guide medical personnel as they insert catheters, stents, or other devices inside the body, treat tumors, or remove blood clots or other blockages.
X rays provide a very reliable diagnosis of bone related injuries such as fractures or fractures dislocations.
They are also very useful in clarification of head injuries following an accident especially in cases of suspected intracranial bleeding.
By means of an angiography, they can provide a quick and effective diagnosis of narrowed blood vessels, thereby decreasing the risk of myocardial infarction.
Need for CT Scan
CT scans are used for a wide range of purposes
Benefits of CT Scan
Unlike traditional X rays which are able to image bones alone, CT scans can provide very detailed and accurate images of several types of tissue, including the lungs, bones and blood vessels. CT scans are painless and non-invasive, which is also a major advantage.
CT scans lead to more effective medical management by determining exactly when surgeries are needed, thus reducing the need for exploratory surgeries.
They improve cancer diagnoses and treatment. Common conditions which are time-sensitive, such as injury, cardiac disease and strokes are also picked up easily and accurately, leading to quick and timely treatment.
During surgery, CT images are a blessing as they guide the surgeon on exactly where to operate. Without this advantage, the success of surgeries could be greatly compromised.
Another huge advantage of the CT scan as opposed to other radiological scans such as the MRI is its ability to rapidly generate images which provide clear and specific information. It is also able to scan either a small portion of the body or the entire body during the same examination.
Major Studies in CT Scan
FAQs on CT :
We use advanced CT scanners with state-of-the-art technology (up to 128 slice scanner) to provide the best quality imaging to help doctors in diagnosis of disease.
We use CT Scan to diagnose multiple disorders like liver, spleen, kidney & bowel. Also, it helps in diagnosis of injuries & internal bleeding in case of accidents.
You will require to follow the instructions of your doctors. The following things might need to be
followed -
- Depending upon the scan, do not eat or drink anything for a few hours before the scan.
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothes, as you may have to change into a gown.
- Remove your jewelry, piercings, eyeglasses, hairpins, dentures before entering the procedure room.
- Inform your doctor about any recent illnesses, diagnosed medical conditions, allergies, and the medications you are taking.
- Inform doctor if you are or may be pregnant
Trained technologists perform the CT scan under the guidance of the Senior Technologist or Radiologist with the usage of well-equipped Workstation.
As per doctor’s advice, you might get a contrast dye which can be administered via arm or hand. This helps the doctor in understanding the body structures more clearly.
Technologist helps you to get prepared & lay down comfortably on the CT scanner table. The CT scanner takes X-Ray images of sections of body from different angles. These images, post-computer processing, results in two-dimensional cross-sectional images of the section of the body examined.
As there is risk of radiation exposure, CT scan should be avoided in pregnant patients
Patients with history of allergies, medical renal disease, cancer chemotherapy and very rarely normal patients might experience reaction to the dye
All the CT scan reports are prepared within minimum assured turnaround time & the hardcopy of the reports & films can be collected at the center where scan was taken.
Need for MRI Scan
An MRI scan is important for several reasons:
Benefits of MRI
An MRI scanner can be used to take images of any part of the body (e.g., head, joints, abdomen, legs, etc.), in any imaging direction. Whereas a CT scan is excellent at imaging bones, an MRI provides better soft tissue contrast than CT and can differentiate better between fat, water, muscle, and other soft tissue.
These images provide information to physicians and can be useful in diagnosing a wide variety of diseases and conditions.
Major Studies in MRI Scan
FAQs on MRI :
We use advanced MRI machines with state-of-the-art technology (up to 3 Tesla scanner) to provide the best quality imaging to help doctors.
MRI is needed in headache, low back ache and in cases of injuries of joints. It also will be required when there is abdominal pain, uterine or ovarian diseases etc
You need to remove all metallic objects including metallic implants, keys, coins, wallet, cards having magnetic strips, all types of jewelry, hair pins.
Detailed clinical history, including previous scan details if there, to be provided Counseling will be provided to you to avoid claustrophobia & you’re required to keep still. Contrast injection risks and benefits will be informed to you & your relative.
Trained technologists perform the MRI Scan under the guidance of the Senior Technologist or Radiologist with the usage of well-equipped Workstation.
As per doctor’s advice, you might get a contrast dye which can be administered via arm or hand. This helps the doctor in understanding the body structures more clearly.
Technologist helps you to get prepared & lay down comfortably on the MRI table.
You might hear a loud noise due to machine generating energy to take images of body. A Headphone could be provided to hush the sound
Pregnant women should avoid MRI scan, especially in the first trimester. Also, contrast die is not recommended for them.
If you have certain metallic object inside the body like clips, pacemakers, cochlear implants or certain metal coils, should not get MRI scan.
All the MRI scan reports are prepared within minimum assured turnaround time & the hardcopy of the reports & films can be collected at the center where scan was taken.
Need for USG:
Preparation required before an ultrasound is very minimal. Depending on the organ to be scanned, you may be required to refrain from eating anything for up to 8 hours before the scan. For a USG during pregnancy, it is important to have a full bladder for scans of an unborn baby or the pelvic region.
Benefits of USG:
Ultrasounds are painless and do not require needles, incisions or injections. They also have no harmful
radiation, making it an excellent choice, especially for children.
The depth of the ultrasound can be monitored and controlled to a large extent, hence making it convenient to scan individuals who cannot be scanned by other methods for some reasons.
In an ultrasound, patients are not exposed to ionizing radiation, thus making the procedure safer than diagnostic techniques such as CTs or X-rays.
Our Major Services in Sonography:
Colour Doppler:
Colour Doppler is a special modality in sonography in which we can examine blood supply/ blood vessels of various organs in body. We can evaluate the obstructions of blood flow and can predict their causes and outcome. Colour Doppler gives us opportunity for prevention and early treatment of certain fatal diseases/ conditions. For example, early diagnosis of carotid artery plaques can give us opportunity for early treatment thereby helps in preventing serious potential conditions like brain infarct. It also helps to diagnose some acute conditions like torsion of testes/ ovaries. This is precious tool in evaluating blood supply of fetus in mother's womb.
Our Major Services in Colour Doppler:
FAQs on USG :
We use higher end USG machines with advanced 2D/3D imaging and with Color Doppler scanning facility.
We use USG imaging to diagnose multiple diseases, lesions, causes of pain, to evaluate blood flow.
USG is important modality to assess fetal growth through various parameters as well as to assess fetal blood flow.
USG is also used for guiding tool for multiple interventional procedures.
Radiologists performs USG & Color Doppler tests. Cardiologist performs 2-D echo test.
Doctor puts probe on your body area which needs to be scanned and moves it in order to get internal organ's images from multiple angles (sections). USG probe sends high frequency pulse and captures it's echo, then USG machine process this data and creates images on machine's screen.
USG is totally safe diagnostic modality with no side effects.
Almost all USG reports are generated in very short span after the procedure.

Need for DEXA scan:
A DEXA scan is primarily conducted to determine a person’s risk of bone fracture and osteoporosis. This scan, which typically focuses on the lower spine and the hips is also used to determine whether your current osteoporosis treatment is effective or not.
A DEXA may be ordered if you are over the age of 70 and exhibit signs of osteoporosis. A broken bone after the age of 50 can also be cause to undergo a DEXA scan.
DEXA scans are typically an outpatient procedure for which no specific preparation is required, except for abstinence from any calcium supplements for 24 hours prior to the test.
Clothing and/or items with metal fasteners, zippers or hooks will need to be taken off, along with jewelery or any other metallic items such as keys. Having undergone a CT scan requiring the use of any contrast material, or a barium exam might need a person to wait a few days before undergoing a DEXA scan.
Benefits of DEXA:
With age, the bones in your body become more brittle and weaker. They end up losing the calcium content in them. One of the primary benefits of doing a DEXA scan is to find out whether you are suffering from osteoporosis, which will prevent disabilities and fractures.
This is an easy, painless, risk-free and non-invasive procedure that takes no more than about 15-20 minutes to complete. This helps in remaining aware of your bone density in order to prevent bone fractures caused due to brittle bones.
Important risk factors for osteoporosis include:
Need for Mammography:
Although a mammography cannot conclusively prove that an abnormal area is breast cancer, it could raise a suspicion, due to which a tissue sample may be sent for further investigations like a biopsy. It is hence advised to undergo this procedure annually when over the age of 40. Finding breast cancer early significantly reduces your risk of dying from the disease by 25-30% or more.
This is particularly helpful since a mammogram can detect lumps 2-3 years before it can be felt by touch.
Where preparation goes, there are a few pointers worth considering before your appointment. Avoid the usage of perfume, lotion or deodorant before the procedure. These can show up as white spots on the screening, leading to inaccurate readings.
Avoid undergoing this procedure directly before or after your menstrual cycle. Your breasts may be more tender/swollen around the time of your period, which can cause extra discomfort during the mammogram. If you are premenopausal, the best time to go is about a week after your period.
It is important to make note of any breast changes, family history or medical history before the procedure.
The American Cancer Society offers the following guidelines to women who are symptom-free:
- Women 20 and older should perform breast self-examinations every month.
- Women 20 to 39 should have a physical breast examination every three years, and women 40 and older should have one every year.
- Women 40 and older should have a mammogram every year, or more often for women at increased risk.
- Women with personal or family histories of breast cancer should consult their doctors about the need for more frequent or earlier mammography. Krsnaa has India's first mammography system which emits no ionizing radiation unlike x-ray mammography or PET/CT.
Benefits of Mammography:
Today, dedicated equipment, used only for breast X-rays, produces studies that are high in quality, but low in radiation dose. Radiation risks are considered to be negligible, even less than a standard chest X ray.
It is used to detect and diagnose breast disease in women who either have breast problems, such as a lump, pain, or nipple discharge. The procedure allows detection of breast cancers , benign tumors, and cysts before they can be detected by palpation (touch).
It works just as well as for women who have no breast complaints.
A mammography is a quick procedure that lasts no more than about 20 minutes. It is a safe procedure that causes minimal discomfort to most women.